
Interview: How This MSP Helped Clients Achieve CMMC Level 2
TeamLogic IT of Melbourne and Vero Beach: Among the First to Guide Clients to CMMC Level 2 For many Managed Service Providers (MSPs), the rollout
Get CMMC Ready
If your small or mid-sized business works with the Department of Defense (DoD), compliance with the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is no longer optional—it’s a requirement. Any company handling Federal Contract Information (FCI) or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) must meet CMMC security standards or risk losing valuable government contracts.
For small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs), achieving compliance comes with a unique set of challenges. How much will it cost? How long will it take? Can you manage it in-house, or do you need a consultant?
This guide breaks down the key considerations, costs, timelines, and risks involved in CMMC compliance. Whether you’re preparing for self-assessment (DIY) or a third-party audit, this information will help you make informed decisions.
For defense contractors, CMMC isn’t just a regulatory hurdle—it’s a business necessity. Failure to comply means losing millions in government contracts, while compliance strengthens cybersecurity, protects sensitive data, and builds a competitive edge.
CMMC 2.0 streamlines the framework into three certification levels, each with specific cybersecurity requirements. Understanding these levels and knowing how to prepare for assessment is critical to staying competitive in the defense sector.
CMMC 2.0 is designed to protect sensitive government data across the entire Defense Industrial Base (DIB). It consists of three levels, each with increasing security requirements:
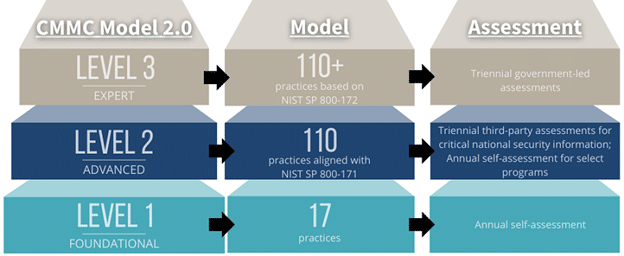
Key Requirements of Level 1
Key Requirements of Level 2
Key Requirements of Level 3
Important Note: The DoD is still refining Level 3 requirements, but companies should focus on achieving full Level 2 compliance first.
2024: Final rule published indicating that SMBs should begin compliance efforts immediately.
2025: DoD starts including CMMC requirements in contracts.
2026-2028: Full rollout— A three-year phased rollout means more contracts will include CMMC requirements as time goes on.
Waiting until the last moment to get certified really isn’t an option as the entire process typically takes 9-12 months. In fact, according to a DIB Contractor Survey, 73% have spent more than 1 year preparing for CMMC and still aren’t done. Being proactive puts you ahead of the curve.

Key Considerations for Small Businesses
If your business fails to comply with CMMC, you could face:
Loss of DoD Contracts – Non-compliance means you can’t bid on new contracts.
Financial Penalties – Potential fines, contract loss, or legal repercussions for security failures.
Cybersecurity Breaches – Without proper security, your company is at higher risk of cyberattacks.
Reputational Damage – A failed assessment or security breach can hurt your business’ credibility.
Factor | DIY (Self-Assessment) | Consultant-Assisted |
Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment, but cost-effective long term |
Time | Takes longer | Faster due to expert guidance |
Compliance Risk | Higher (risk of errors) | Lower (expert ensures compliance) |
Best for | Level 1 businesses with strong IT teams | Level 2 businesses or those needing guidance |
Step 1: Determine Your CMMC Level
Pro Tip: Start your CMMC Level 2 prep at least 6-12 months before your assessment!
Step 2: Conduct a CMMC Gap Analysis
Identify missing security controls and create a remediation plan to fix weaknesses before an assessment.
A gap analysis identifies where your current cybersecurity posture falls short of CMMC requirements. This helps you proactively address deficiencies before an official assessment.
As a Cyber-AB Registered Practitioner Organization (RPO), Alluvionic’s CMMC gap analysis services provide defense contractors with a clear, actionable roadmap to CMMC Level 1 or Level 2 certification, ensuring you meet Department of Defense (DoD) cybersecurity requirements without unnecessary costs or delays.
Step 3: Remediate CMMC Gaps
A CMMC gap analysis is like a cybersecurity health check—it identifies the vulnerabilities in your systems, policies, and processes. But just knowing the problems isn’t enough. Remediation is where the real work happens.
CMMC remediation is the process of:
For companies with limited internal cybersecurity resources, remediation can feel like an insurmountable challenge. You have contracts to fulfill, projects to complete, and employees to manage—you can’t afford a security project that drags on for months and drains your budget. RPOs, like Alluvionic, can lead the remediation effort, ensuring compliance while minimizing disruption to your business.

Step 4: Prepare for CMMC Assessments
Depending on your CMMC level, you’ll need to undergo self-assessments or third-party assessments to maintain compliance.
Assessment Types by Level:
How to Prepare:
Working with a Cyber-AB Registered Practitioner Organization (RPO) like Alluvionic will help ensure readiness.
We Make CMMC Crystal Clear
No jargon. No confusion. Just a simple step-by-step process to help IT companies get compliant without the headache.
Trusted by 125+ Government Contractors
We’ve helped IT firms, MSPs, and cybersecurity companies navigate DFARS, NIST, and CMMC, eliminating wasted time and stress.
An Established CMMC Partner
As a Cyber-AB RPO since 2021, we’ve been doing CMMC right since day one.
Women-Owned. Small Business Focused.
We understand the challenges small & mid-sized MSPs face, and we tailor solutions to fit your budget and timeline.
Don’t wait until CMMC requirements delay your contract eligibility. Take proactive steps to secure your business and remain competitive.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward securing your CMMC certification.

TeamLogic IT of Melbourne and Vero Beach: Among the First to Guide Clients to CMMC Level 2 For many Managed Service Providers (MSPs), the rollout

ICYMI: Behind the Scenes of a Successful CMMC Level 2 Assessment For small to mid-sized government contractors navigating the CMMC landscape, it’s easy to feel

When the U.S. Space Force (USSF) needed to modernize its outdated, paper-based rocket launch checklists, they turned to Alluvionic, and the result was out
Step 2: Conduct a CMMC Gap Analysis
Identify missing security controls and create a remediation plan to fix weaknesses before an assessment.
A gap analysis identifies where your current cybersecurity posture falls short of CMMC requirements. This helps you proactively address deficiencies before an official assessment.
How to Perform a Gap Analysis:
As a Cyber-AB Registered Practitioner Organization (RPO), Alluvionic’s CMMC gap analysis services provide defense contractors with a clear, actionable roadmap to CMMC Level 1 or Level 2 certification, ensuring you meet Department of Defense (DoD) cybersecurity requirements without unnecessary costs or delays.
The race to compliance has already begun—don’t fall behind. Alluvionic’s experts provide cybersecurity support and focused change management. We minimize disruptions, ensure smooth adoption, and set your business up for success.
"*" indicates required fields






It’s simple. A project that gets off on the right foot is likely to take a successful journey. So why do so many projects fail? Use this checklist to assure your project succeeds from the beginning.

Whether you need project management, process improvement, cybersecurity, product development, training, or government services, Alluvionic has the expertise to provide Peace of Mind and Project Assurance®.
"*" indicates required fields
PMI®, PMP®, CAPM® and PMBoK® are registered marks of the Project Management Institute
NAICS Codes: 541611, 541330, 541511, 541512 ,541519, 541613, 541614, 541618, 541990, 561990, 611420, 611430, 813910, 813920